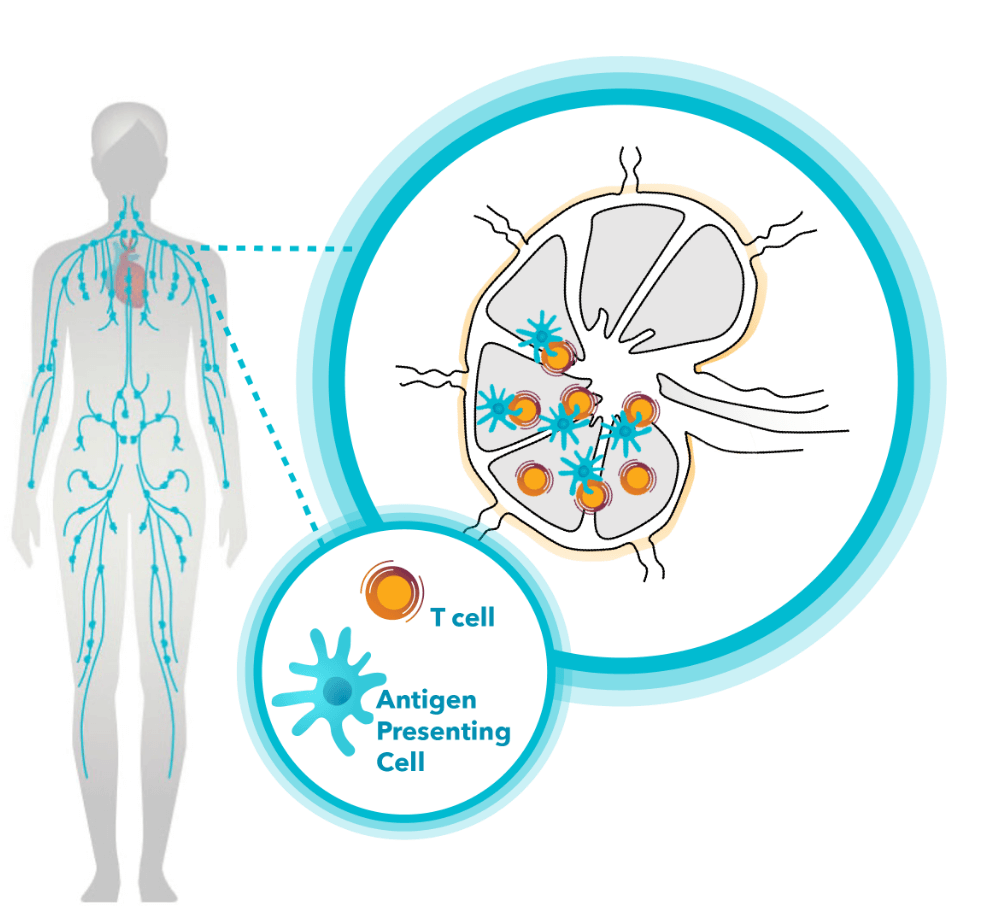
Lymph nodes: the center of the immune response
Lymph nodes are small, highly organized structures filled with diverse and specialized groups of immune cells. Positioned strategically throughout the body at the confluences of lymphatic vessels, they collect and filter lymphatic fluid for signs of danger, including traces of cancer or infectious pathogens. Known as the “command center” of the immune system, the lymph nodes play a vital role in detecting harmful threats to our health and coordinating the buildup of protective immune responses.
Proper education, multiplication, and activation in the lymph nodes is critical for preparing disease-fighting immune cells for deployment throughout the body to resolve disease. Numerous key immune cells, including antigen-presenting cells (APCs), T cells, and B cells, are organized in the lymph nodes. These cells are in constant communication, exchanging complex biological signals as they monitor our health. APCs serve as immune-sentinels, constantly sampling lymph fluid for signs of danger.1,2
When disease is detected, APCs coordinate the buildup of a highly trained battalion of protective immune cells. T cells and B cells matched to the detected threat are activated, educated, and deployed from the lymph nodes to locate and eliminate disease.1,2
Effective orchestration of interactions between immune cells in the lymph nodes ultimately determines the magnitude, specificity, and persistence of the immune response developed to fight disease.
Targeting the lymph nodes: a novel approach to immunotherapy
While highly understood, we believe the critical role of the lymph nodes in charging the immune response remains underutilized in immuno-oncology. At Elicio, we are working to harness the natural power of the lymph nodes to amplify the immune response, with the potential of offering patients a stronger fight against cancer.
By engaging the most potent sites of immune cell education and activation, our Amphiphile (AMP) platform is built to enhance T-cell proliferation and function, generating more potent antitumor immune responses.
References
- Liao S, von der Weid PY. Lymphatic system: an active pathway for immune protection. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;38:83-89.doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.11.012
- Grant SM, Lou M, Yao L, Germain RN, Radtke AJ. The lymph node at a glance – how spatial organization optimizes the immune response. J Cell Sci. 2020;133(5):jcs241828. Published 2020 Mar 6. doi:10.1242/jcs.241828